
Back EIDAS Catalan EIDAS Czech Verordnung (EU) Nr. 910/2014 (eIDAS-Verordnung) German EIDAS Spanish EIDAS Estonian Electronic identification and trust services French EIDAS Italian 規則 (EU) No 910/2014 Japanese EIDAS Korean EIDAS Dutch

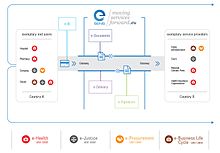
eIDAS (for "electronic IDentification, Authentication and trust Services") is an EU regulation with the stated purpose of governing "electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions". It passed in 2014 and its provisions came into effect between 2016 and 2018.[1][2]
In 2023, a proposed change to the law would allow any EU government to perform man-in-the-middle attacks and spy on all internet messages, including encrypted communications.[3] The proposal was condemned by groups of cyber security researchers, NGOs, and civil society, as a threat to human rights, privacy, and dignity.[4][5][6]
- ^ Turner, Dawn. "Understanding eIDAS". Cryptomathic. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- ^ "Regulation (EU) No 910/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 July 2014 on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the internal market and repealing Directive 1999/93/EC". EUR-Lex. The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Retrieved 18 March 2016.
- ^ https://blog.mozilla.org/netpolicy/files/2023/11/eIDAS-Industry-Letter.pdf
- ^ https://last-chance-for-eidas.org/
- ^ https://nce.mpi-sp.org/index.php/s/cG88cptFdaDNyRr
- ^ https://www.internetsociety.org/resources/doc/2023/qualified-web-authentication-certificates-qwacs-in-eidas/
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search